What Causes Hair Loss in Men According to Dermatologists?

Hair loss in men is a common issue that affects a significant percentage of the male population. It can be a frustrating and distressing experience, and many men may feel self-conscious or embarrassed about their hair loss. Understanding the causes of hair loss in men can help find the proper treatment or solution to restore or maintain healthy hair growth. In this blog post, we will explore the various causes of hair loss in men and the available options for treatment and prevention.
Most Common Causes of Hair Loss in Men
Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA)
Androgenetic alopecia (AGA), known as male pattern baldness, affects 30 to 58 percent of men over 50. It is the most common cause of hair loss in men. AGA is caused by a combination of genetic and hormonal factors, and it typically affects men with a family history of hair loss.
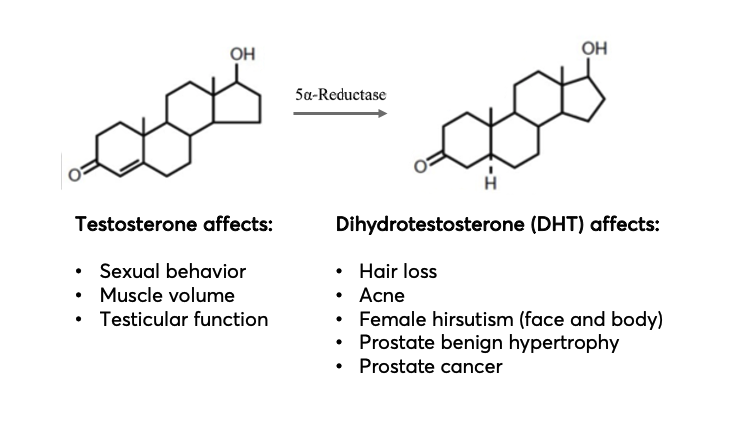
AGA is characterized by a receding hairline and thinning of hair on the crown, which eventually leads to complete baldness. The condition is caused by an enzyme called 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT is a hormone that causes hair follicles to shrink, leading to hair loss.
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT)
Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a hormone that plays a key role in male pattern baldness. DHT is a byproduct of the male hormone testosterone, and it attaches to the hair follicles on the scalp, causing them to shrink. As the hair follicles shrink, they produce thinner and weaker hair, eventually leading to hair loss. DHT, the main cause of hair loss in AGA, acts by inducing the production of interleukin (IL-) 6 and transforming growth factor (TGF-) β2 by dermal papilla cells (DPCs). Therefore, it suppresses hair growth and premature initiation of the catagen phase (Umar S et al., 2021).
Less Common Causes of Hair Loss in Men
Telogen Effluvium
Telogen effluvium is a temporary hair loss condition due to a change in the hair growth cycle. Stress, hormonal changes, nutrient deficiencies, or certain medications can cause it. During the telogen phase, hair is in a dormant state, and it eventually falls out. In individuals with telogen effluvium, the hair growth cycle is disrupted, and more hair falls out than usual, leading to hair loss. The most common treatments for telogen effluvium include addressing the underlying cause, reducing stress, and ensuring proper nutrition. In some cases, minoxidil may be recommended to stimulate hair growth.
Nutritional Deficiencies
Nutritional deficiencies can also cause hair loss. A diet deficient in specific vitamins and minerals, such as iron, zinc, and vitamin D, can lead to hair loss. Inadequate protein intake can also cause hair loss. The most common treatment for hair loss due to nutritional deficiencies is to supplement the diet with the lacking nutrients, such as iron, zinc, or vitamin D supplements. A balanced diet rich in essential nutrients can also help promote healthy hair growth.
Scalp Infections
Scalp infections, such as fungal or bacterial infections, can cause inflammation of the hair follicles, leading to hair loss. The most common treatments for hair loss due to scalp infections include topical or oral antifungal or antibacterial medications to eradicate the disease. Once the infection is treated, hair growth should resume.
Medications
Certain medications can also cause hair loss as a side effect. Medications used to treat conditions such as high blood pressure, depression, and gout can cause hair loss. The most common treatment for hair loss due to medication is to consult with a healthcare professional about potentially changing the medication or adjusting the dosage. Sometimes, hair loss may resolve once the medication is stopped or modified.
Bodybuilding
Male pattern hair loss is influenced by the levels of testosterone and DHT, and weightlifting can increase testosterone levels. However, the primary cause of male pattern hair loss is a genetic predisposition, with a natural increase in testosterone and DHT. Although weightlifting can lead to a slight rise in these hormones, it is not expected to cause additional hair loss.
That being said, individuals who use testosterone or other steroids for bodybuilding can indeed affect the hair on their head and body in several ways:
1. Androgenic Alopecia: Anabolic steroids can trigger androgenic alopecia, commonly known as male pattern baldness. A receding hairline and thinning of hair on the crown of the head characterize this condition. It is more common in individuals with a genetic predisposition to hair loss.
2. Accelerated Hair Loss: Steroids can expedite hair loss in individuals prone to androgenic alopecia. If someone has a family history of baldness, the use of steroids can exacerbate the condition and lead to quicker hair thinning.
3. Excessive Body Hair Growth: In some cases, steroid use can cause hirsutism, which is excessive hair growth on the body, including areas where hair growth is typically minimal in both men and women.
4. Changes in Hair Texture: Some users may notice changes in the texture of their hair while taking anabolic steroids. It might become coarser, drier, or more brittle.
5. Temporary Hair Shedding: Anabolic steroids can trigger a condition called telogen effluvium, leading to temporary hair shedding. This occurs when a large number of hair follicles enter the resting phase simultaneously due to the hormonal changes induced by steroids.
It's important to understand that the impact of steroids on hair can vary from person to person. Not everyone who uses steroids will experience significant hair loss or changes in hair growth patterns. Still, those genetically susceptible to hair loss are more likely to be affected.
Stress
Stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle and trigger telogen effluvium. Stress can also cause an increase in the levels of hormones such as cortisol, which can lead to hair loss. The most common treatments for stress-related hair loss include stress management techniques, such as meditation, exercise, or therapy, and ensuring adequate sleep and nutrition.
Environmental Factors
Environmental factors such as pollution, UV radiation, and exposure to harsh chemicals can damage the hair follicles and lead to hair loss. The most common treatments for hair loss due to environmental factors include reducing exposure to harmful elements, using gentle hair care products, and protecting the hair and scalp from sun damage. Incorporating hair-protective measures, such as wearing a hat or using hair sunscreen, can help minimize the impact of environmental factors on hair health.
Alopecia Areata
Alopecia areata is an autoimmune disorder that occurs when the immune system attacks the hair follicles, causing hair loss. Alopecia areata can cause hair loss on the scalp and other body areas.
The most common treatments for alopecia areata include corticosteroid injections, topical immunotherapy, and oral medications, such as corticosteroids or immunosuppressants, to suppress the immune system's attack on hair follicles. In some cases, light therapy may also be recommended to help stimulate hair regrowth.
What are the Best Treatments for Male Pattern (Androgenetic) Hair Loss?
Finasteride
Finasteride is a medication that is commonly used to treat male pattern baldness. It works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT. By reducing the levels of DHT, finasteride can help to prevent hair loss. Oral finasteride may cause a range of adverse effects in some individuals, including sexual side effects like reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculation disorders. Other potential side effects include mood changes, such as depression and anxiety, as well as breast tenderness or enlargement. It is important to note that while these side effects may occur, they are not experienced by all users, and many people take finasteride without issue.
Minoxidil
Topical minoxidil 5% is an FDA-approved treatment for male pattern hair loss, offering a non-invasive solution for many individuals. This over-the-counter medication stimulates hair growth and can be effective for various stages of hair thinning. Some possible side effects of minoxidil include skin irritation, itching, and redness.
Plant-Based Scalp Treatment Serums with DHT Blockers
These scalp treatment serums harness the power of potent botanical ingredients that stimulate hair growth and promote overall health. One example of this kind of serum is the MDhair Regrowth Serum, formulated with 20 active plant ingredients, targeting various aspects of scalp and hair health.
Hair Growth Supplements
Hair growth supplements can also be used to treat hair loss. These supplements can give the body the necessary vitamins and minerals to promote hair growth. Specially formulated for men and women with androgenetic alopecia, the MDhair Regrowth Supplements include potent DHT blockers that can help reduce the effects of DHT on hair follicles and support hair regrowth.
Collagen Peptides
Collagen peptides can offer multiple benefits for men with hair loss, including promoting hair growth, strength, and thickness by supporting keratin production, a vital structural protein in hair. Additionally, collagen can enhance skin elasticity and contribute to reducing joint pain.
The takeaway:
Various factors, including genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, and certain medical conditions, can cause hair loss in men. Understanding the cause of hair loss is essential in finding the proper treatment or solution. Many options for treating and preventing hair loss are available, including medication, hair growth supplements, hair restoration treatments, and trichology. If you are experiencing hair loss, speaking with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and find the proper treatment or solution is essential.
FAQS:
Q1. What is the most common cause of hair loss in men?
A1. The most common cause of hair loss in men is Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA), also known as male pattern baldness.
Q2. How does Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA) cause hair loss in men?
A2. A combination of genetic and hormonal factors causes Androgenetic Alopecia (AGA). An enzyme called 5-alpha reductase converts testosterone into dihydrotestosterone (DHT), which shrinks hair follicles, leading to hair loss.
Q3. What is Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) and its role in hair loss?
A3. Dihydrotestosterone (DHT) is a hormone derived from testosterone that attaches to hair follicles on the scalp, causing them to shrink. This results in thinner and weaker hair and eventually leads to hair loss.
Q4. Are there any less common causes of hair loss in men?
A4. Yes, there are less common causes of hair loss in men, including Telogen Effluvium, nutritional deficiencies, scalp infections, medications, stress, environmental factors, and Alopecia Areata.
Q5. What is Telogen Effluvium?
A5. Telogen Effluvium is a temporary hair loss condition caused by disruptions in the hair growth cycle. Stress, hormonal changes, nutrient deficiencies, or certain medications can trigger it.
Q6. Can nutritional deficiencies contribute to hair loss in men?
A6. Yes, nutritional deficiencies, particularly deficiencies in vitamins and minerals like iron, zinc, and vitamin D, can lead to hair loss in men. Inadequate protein intake can also be a contributing factor.
Q7. Can scalp infections cause hair loss in men?
A7. Yes, scalp infections, such as fungal or bacterial infections, can cause inflammation of the hair follicles and result in hair loss.
Q8. Can certain medications cause hair loss in men?
A8. Certain medications used to treat conditions like high blood pressure, depression, and gout can cause hair loss as a side effect.
Q9. Can stress contribute to hair loss in men?
A9. Yes, stress can disrupt the hair growth cycle and trigger a condition called telogen effluvium, leading to increased hair loss. Stress can also affect hormone levels, such as cortisol, further contributing to hair loss.
Q10. Can environmental factors play a role in hair loss among men?
A10. Yes, environmental factors such as pollution, UV radiation, and exposure to harsh chemicals can damage the hair follicles and contribute to hair loss in men.
Q11. What is Alopecia Areata?
A11. Alopecia Areata is an autoimmune disorder in which the immune system attacks the hair follicles, resulting in hair loss. It can affect the scalp and other areas of the body.
Q12. What are the best treatments for male pattern (Androgenetic) hair loss?
A12. Some of the best treatments for male pattern (Androgenetic) hair loss include finasteride, minoxidil, plant-based scalp treatment serums with DHT blockers, hair growth supplements, and collagen peptides.
Q13. How does finasteride work to treat male pattern baldness?
A13. Finasteride works by inhibiting the enzyme 5-alpha reductase, which converts testosterone into DHT. By reducing DHT levels, finasteride can help prevent hair loss.
Q14. What are the potential side effects of finasteride?
A14. Potential side effects of finasteride may include sexual side effects such as reduced libido, erectile dysfunction, and ejaculation disorders, as well as mood changes and breast tenderness or enlargement. It's important to note that not all users experience these side effects, and many people take finasteride without any issues.
Q15. How does minoxidil help in treating male pattern hair loss?
A15. Minoxidil is a topical medication that stimulates hair growth and is FDA-approved for male pattern hair loss. It can be effective at different stages of hair thinning. Some possible side effects of minoxidil include skin irritation, itching, and redness.
Q16. What are plant-based scalp treatment serums with DHT blockers?
A16. Plant-based scalp treatment serums with DHT blockers are formulated with potent botanical ingredients that stimulate hair growth and promote scalp and hair health. These serums, like the MDhair Regrowth Serum, contain active plant ingredients targeting various aspects of hair health.
Q17. How do hair growth supplements help in treating hair loss?
A17. Hair growth supplements provide the body with the necessary vitamins and minerals that promote hair growth. The MDhair Regrowth Supplements, formulated for men and women with androgenetic alopecia, include potent DHT blockers to reduce the effects of DHT on hair follicles and support hair regrowth.
Q18. Can collagen peptides benefit men with hair loss?
A18. Yes, collagen peptides can promote hair growth, strength, and thickness by supporting keratin production, a vital protein in hair. Collagen can also enhance skin elasticity and contribute to reducing joint pain.
Q19. What is the key takeaway regarding hair loss in men?
A19. Understanding the causes of hair loss in men is crucial for finding the appropriate treatment or solution. Genetic predisposition, hormonal imbalances, medical conditions, and lifestyle factors can contribute to hair loss. Consulting with a healthcare professional to determine the cause and explore treatment options is essential for addressing hair loss effectively.
Q20. Why do men experience baldness more than women?
Women produce far less DHT and testosterone than men. Young women also have higher amounts of the hormones estrogen and progesterone, both of which play a protective role in keeping hair follicles healthy and functioning. With age, and especially after menopause, estrogen and progesterone levels in women decrease, and testosterone levels become more dominant, increasing the prevalence and severity of female pattern hair loss.
More info:
Best hair growth supplements for men
Best natural treatments for hair loss in men - 2023
Best Hair Oil for Men - according to Dermatologists
Find the most effective hair growth products for you by taking the free hair assessment.



